Poltava, prospekt Vitaliia Hrytsaienka 9 Weekdays: 8:30-15:00, Weekend: weekend +38 (0532) 56-02-11+38 (095) 688 25 07
Testicular prosthetics: at what age can the operation be performed and whether it is needed
 The absence of a testicle after surgery, or its congenital developmental defects is a common cause of not only physical discomfort in men, but also many complexes and psychological problems, including those affecting sexual and social health.
The absence of a testicle after surgery, or its congenital developmental defects is a common cause of not only physical discomfort in men, but also many complexes and psychological problems, including those affecting sexual and social health.
Surgery to place an implant is called a testicular prosthesis. This is a fairly simple and quick operation that does not require a long recovery period and has a pronounced cosmetic effect. While the insertion of a prosthesis into the scrotum restores the aesthetic appearance of the genitals, this intervention does not in any way affect the functioning of the male reproductive system.
Nevertheless, both parents of boys and adolescents with congenital disorders of the development of this organ and adult patients often apply for testicular prosthetics. The placement of the implant allows you to correct the asymmetry that has arisen as a result of both congenital conditions and after operations such as orchiectomy.
When is surgery necessary?
The implantation of a prosthesis into the scrotum is indicated for conditions characterized by the absence of one or two testicles. Among them are congenital developmental pathologies, removal of the testicles after operations, trauma or severe inflammation, which led to deformation of the organ.
Since such conditions are characterized by a violation of the psychological state of a man and are often accompanied by uncertainty and problems in the sexual sphere, the cosmetic effect of such an intervention has a positive effect on the quality of life of these patients.
What are the indications and contraindications for testicular prosthetics?
As already mentioned, this operation does not affect reproductive function and has a purely cosmetic effect. Among the conditions in which prosthetics may be needed, there are congenital:
- monorchia - the absence of one testicle as a result of intrauterine growth disorders;
- anorchia - the absence of both testicles for the same reason;
- cryptorchidism is a condition in which the descent of the testicle into the scrotum is impaired in early childhood.
In addition, some diseases and injuries also lead to the absence of one or two testicles and are an indication for implantation of a prosthesis:
- testicular atrophy as a result of an inflammatory or other disease;
- trauma or volvulus of the testicles followed by amputation;
- cancer followed by amputation of one or two testicles.
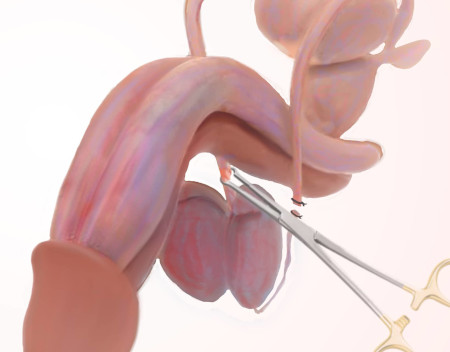 Since this operation is intended solely for the correction of a morphological defect, there are no absolute contraindications to it. However, the intervention is prohibited for a number of conditions:
Since this operation is intended solely for the correction of a morphological defect, there are no absolute contraindications to it. However, the intervention is prohibited for a number of conditions:
- acute infectious diseases and exacerbation of chronic and systemic;
- a history of diabetes mellitus in a state of decompensation;
- mental disorders;
- the presence of morphological defects in the tissues of the scrotum and testicle - seals, cysts and other conditions that require additional consultation with a urologist;
- lack of tissue of the scrotum for plastic surgery, which does not allow for prosthetics to be carried out in full.
The operation itself has a short duration - up to 50 minutes - and takes place under local anesthesia using a strong anesthetic. At the consultation of the surgeon, it is necessary to find out the presence of an allergic reaction to novocaine, so that it is possible to choose a safe and effective pain reliever.
Sutures after prosthetics often heal in a couple of days, and after a few weeks they cease to be noticeable, leaving not a single unpleasant reminder of the previous operation.
What is the best age for this operation?
The question often arises whether it is worth doing testicular prosthetics for a child, or is it better to wait until the boy grows up and can make a decision on his own.
In some cases - for example, with cryptorchidism - early treatment reduces the risk of more formidable complications: cancer and infertility. For this reason, such an operation is allowed, including for children.
In addition, many urologists believe that implantation of a prosthesis in boys with indications for it should take place at the age of about five years or before the onset of puberty. Thus, it is possible to prevent underdevelopment of the scrotum and avoid psychological problems during and after the first sexual intercourse.
Another issue that worries parents is the size of the implant, because the size of the testicle also changes with age. If a prosthesis is implanted in childhood, it may be necessary to replace it with an implant of a different size in adolescence. Scrotal plastic is not required in this case - the prosthesis at the time of replacement has already taken root enough and is easily replaced with another.
specialists of the Clinic for Plastic Surgery
22-06-2021
Similar news
